Pregnancy-related deaths are a critical concern in the United States, where the maternal mortality rate continues to rise alarmingly, making it the highest among high-income countries. Over 80% of these deaths are preventable, highlighting significant flaws in our healthcare system that leave many women vulnerable to complications during and after childbirth. Healthcare disparities play a substantial role in these statistics, with alarming differences in mortality rates based on race and geography, particularly affecting American Indian and Alaska Native women. Furthermore, the prevalence of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease during pregnancy raises pressing questions about the adequacy of prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing these issues is imperative, not just to prevent unnecessary maternal mortality but also to ensure a healthier future for mothers and their children alike.
Maternal deaths associated with pregnancy complications remain an urgent public health issue, as the United States grapples with unacceptable rates of mortality during and following childbirth. Many of these fatalities, often classified as preventable deaths, reveal stark disparities influenced by socioeconomic and racial factors. The increase in late maternal deaths is particularly concerning, underscoring the need for comprehensive postpartum care that extends well beyond the initial weeks after delivery. Chronic health issues, including cardiovascular conditions, are surfacing among younger populations, complicating their experiences of maternity. Tackling these multifaceted challenges requires systemic improvements in healthcare delivery and policies that prioritize the wellbeing of all mothers.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
In the United States, the alarming statistics related to pregnancy-related deaths reveal a low point in maternal health. With a maternal mortality rate surpassing that of other high-income countries, it’s crucial to comprehend the factors contributing to this crisis. Researchers highlight that over 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, indicating a substantial opportunity for improvement through increased healthcare access and education regarding maternal care. Underlying systemic issues, such as healthcare disparities and socioeconomic factors, significantly influence these outcomes, making it imperative to address the root causes of this preventable epidemic.
The study conducted by the National Institutes of Health sheds light on the increasing trends in pregnancy-related deaths, with the sharpest rise observed during the COVID-19 pandemic. This indicates a troubling intersection between public health crises and maternal health, where existing vulnerabilities become exacerbated. The research suggests that targeted interventions must be taken to provide comprehensive maternal care, especially in vulnerable populations that experience higher mortality rates. Addressing healthcare disparities not only promotes equity but directly impacts maternal health outcomes.
The Impact of Healthcare Disparities on Maternal Mortality
Healthcare disparities play a significant role in the maternal mortality rates observed across different racial and ethnic groups in the U.S. The stark reality is that American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates, almost four times greater than their white counterparts. This disparity is rooted in a combination of socioeconomic determinants, access to quality healthcare, and systemic discrimination that has persisted over the years. To combat this issue, researchers emphasize the need for culturally competent care and policies aimed at reducing barriers faced by high-risk populations.
Efforts to address healthcare disparities through targeted programs can potentially reduce the maternal mortality rate significantly. For instance, adopting successful strategies from states with lower rates, like California, could provide a framework for implementing effective policies nationwide. Additionally, fostering partnerships between different healthcare providers and community health organizations can enhance outreach and support for pregnant individuals and their families, ensuring they receive necessary prenatal and postpartum care.
The Need for Improved Prenatal and Postpartum Care
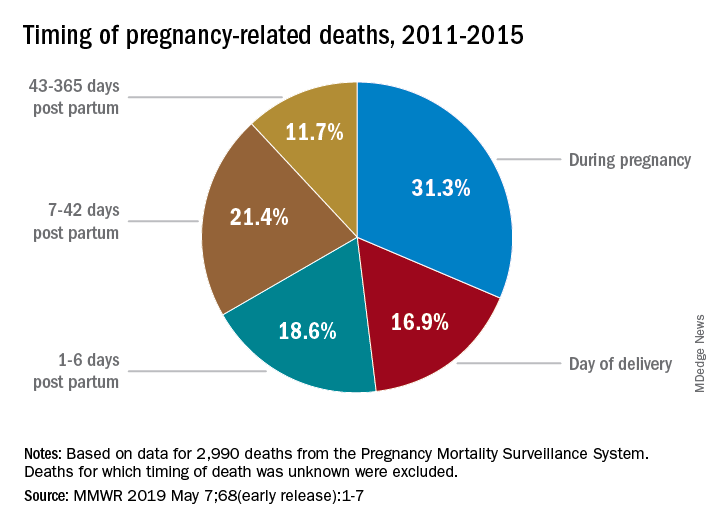
The rising trend in pregnancy-related deaths underscores the urgent need for enhanced prenatal and postpartum care. A significant finding from the research illustrates that a considerable percentage of maternal deaths occurs during the extended postpartum period, pointing to gaps in care that extend beyond the delivery room. Optimizing care around the time of childbirth can prevent many of these deaths. Strategies such as proactive monitoring for cardiovascular diseases and other chronic conditions plaguing many new mothers should be prioritized in health policies and practices.
Moreover, it is essential to view postpartum care as a continuum rather than a finite period that ends a few weeks after birth. Healthcare providers should include systems for long-term support and follow-up for new mothers, particularly those with pre-existing conditions or risk factors for ICU admission. By investing in robust postpartum resources and support networks, we can assure maternal safety and health long after childbirth, ultimately reducing the risk of preventable deaths.
Addressing Cardiovascular Disease During Pregnancy
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of maternal mortality, contributing to over 20 percent of pregnancy-related deaths. This shift from traditional causes such as hemorrhage highlights the changing landscape of maternal health. Recent studies indicate that chronic conditions like hypertension are affecting younger individuals, raising concern about the necessity for early screening and management of these health issues. As healthcare providers identify cardiovascular disease in pregnant individuals earlier, they can tailor treatments and interventions that are crucial for the health of both mother and child.
As we refine our understanding of the intersection between pregnancy and cardiovascular health, it becomes evident that integrated care models that focus on both obstetric and cardiac health are essential. Training healthcare providers to recognize the signs of cardiovascular complications and providing the necessary resource to intervene early can significantly reduce risks. Furthermore, community education initiatives that inform pregnant individuals about cardiovascular health risks and encourage routine check-ups are necessary to prevent adverse outcomes.
Enhancing Awareness Around Maternal Health
Raising awareness about maternal health issues, especially concerning preventable pregnancy-related deaths, is paramount. Public campaigns can serve to inform individuals about the importance of prenatal and postpartum care, the signs of complications, and the critical nature of follow-up and healthcare accessibility. Also, community health organizations should collaborate with healthcare providers to offer workshops, resources, and education to expectant and new mothers on recognizing risk factors.
The growing emphasis on maternal health awareness also ties into larger conversations about social determinants of health, where access to care is intertwined with socioeconomic factors. These initiatives can empower communities to advocate for better maternal healthcare policies and ensure that systemic inequalities are addressed, leading to healthier outcomes. By elevating the focus on maternal health, we can drive change that prioritizes the safety and well-being of mothers across the nation.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure in Maternal Health
The public health infrastructure is critical in addressing maternal health issues, yet it’s currently at risk due to funding cuts and deprioritization of pregnancy-related initiatives. Ensuring the continuity of investment in maternal health programs and research is vital to create impactful changes in maternal mortality rates. Without a robust public health system to track, monitor, and analyze maternal deaths accurately, our understanding of the scope of the problem remains limited, affecting effective solutions.
Moreover, states must collaborate to establish best practices and share successful interventions widely to bolster maternal health across the board. This could create a unified approach to tackle disparities in maternal mortality rates. Advocating for comprehensive policy reforms that emphasize the importance of maternal health can lead to systemic transformations and healthier outcomes for mothers and their children.
Innovations in Maternal Health Care Delivery
The field of maternal healthcare is evolving, with innovative solutions emerging to tackle prevalent problems impacting maternal mortality rates. Telehealth, for instance, offers an avenue to provide remote prenatal and postpartum consultations, particularly for those in underserved areas where access is limited. By utilizing technology, healthcare providers can ensure that mothers receive the necessary care, support, and education even when they cannot attend in-person appointments regularly.
Additionally, integrating multidisciplinary teams that include obstetricians, midwives, mental health specialists, and even social workers can provide a more comprehensive approach to maternal healthcare. Such collaborations help address diverse needs that go beyond medical care, ensuring mothers receive the support they require during their pregnancy and in the postpartum stage. By focusing on holistic care, we can foster resilience and better health outcomes for mothers, reducing the overall rates of preventable deaths.
State-Level Policies and Their Impact on Maternal Health
State-level policies play a crucial role in influencing maternal health outcomes, as disparities among states lead to inconsistencies in care quality and access. For instance, California’s lower maternal mortality rates suggest it has implemented effective policies that other states could replicate. Understanding the specific policy frameworks that contribute to these successes can guide other states toward better health outcomes and help establish national standards.
Furthermore, conducting comprehensive evaluations of maternal health programs and initiatives at the state level can identify best practices and highlight areas in need of improvement. This type of analysis is essential for lawmakers who strive to create policies that accurately respond to the needs of their constituents. Advocacy for equitable health policies can ultimately enhance the overall quality of maternal care across the United States.
Importance of Comprehensive Maternal Health Data
Accurate and comprehensive data on maternal health is essential for understanding the factors contributing to pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. The introduction of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates marks a significant advancement in tracking these vital statistics. This data can provide insights into mortality trends, highlight areas of concern, and help policymakers identify necessary changes within the healthcare system to improve maternal outcomes.
However, until adequate data collection systems are established in all states, the country will struggle to fully grasp the extent of maternal mortality issues. A well-structured approach that encompasses a wider range of timeframes surrounding pregnancy can provide clearer insights into the factors leading to late maternal deaths. Without robust data, programs aimed at reducing maternal mortality rates may lack the specificity needed to implement targeted, effective interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The primary cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. is cardiovascular disease, accounting for over 20% of these preventable deaths. Other common causes include hemorrhage and complications related to chronic conditions such as hypertension. Addressing these issues is crucial to reducing maternal mortality rates.
How significant are the disparities in maternal mortality rates associated with pregnancy-related deaths?
Disparities in maternal mortality rates are significant in the U.S., with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates of pregnancy-related deaths, nearly four times higher than white women. These disparities highlight the need for equitable healthcare access and tailored interventions to improve outcomes across different racial and ethnic groups.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is essential in addressing pregnancy-related deaths, particularly late maternal deaths that occur up to a year postpartum. Enhanced support and healthcare systems designed to monitor women beyond the traditional six-week follow-up can significantly reduce these preventable deaths.
How can the U.S. improve its maternal health outcomes regarding pregnancy-related mortality?
To improve maternal health outcomes, the U.S. needs to invest in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions for quality care during pregnancy and the postpartum period. This includes addressing healthcare disparities, enhancing policy measures, and increasing access to comprehensive maternal health services.
What impact has the COVID-19 pandemic had on pregnancy-related deaths?
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated trends in pregnancy-related deaths, with significant increases noted during 2021. The stresses and challenges faced during the pandemic may have contributed to the rise in maternal mortality rates, underlining the vulnerability of expectant and new mothers during such crises.
Why is it important to consider late maternal deaths in discussions about pregnancy-related mortality?
Considering late maternal deaths is important as they represent a significant portion of pregnancy-related deaths, highlighting deficiencies in postpartum healthcare. Acknowledging these deaths calls for a more comprehensive approach to maternal health, advocating for services that extend beyond immediate postpartum care.
What are the statistics on pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with pregnancy-related deaths rising from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. This troubling trend emphasizes the urgent need for systemic changes in maternal healthcare.
How does cardiovascular disease relate to pregnancy-related deaths?
Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., stemming from chronic conditions like hypertension that affect more women at younger ages. Awareness and management of cardiovascular health during pregnancy are vital for reducing these preventable deaths.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries; rates have been rising since 2018. |
| The leading cause of pregnancy-related death is cardiovascular disease, accounting for over 20% of deaths. |
| American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest mortality rates, nearly four times higher than white women. |
| Disparities in maternal mortality rates vary significantly by state, race, and ethnicity. |
| Late maternal deaths (from 42 days to 1 year postpartum) account for nearly one-third of all pregnancy-related deaths. |
| A systematic national tracking for maternal deaths began only in 2018. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. continue to rise alarmingly, making it imperative to address the underlying factors contributing to this issue. The persistence of such a high maternal mortality rate among high-income countries illustrates a systemic problem requiring urgent reforms. Investing in enhanced prenatal and postpartum care, addressing racial and geographical disparities, and recognizing the importance of late maternal deaths are crucial steps forward. By committing to these changes, we can significantly reduce the preventable deaths linked to pregnancy and enhance maternal health outcomes across the nation.